

On the other hands, there is no index based structure in the list implement byLinkledList. Accessing elements from the list implemented using ArrayList is faster as it has an index-based data structure.ArrayList class implements List interface whereas, the LinkedList class implements List, Queue, and Deque interfaces.The ArrayList extends the AbstractList class which is also a Collection class whereas, the LinkedList class extends AbstractSequentialList class that is again a Collection class.However, the internal data structure used by the LinkedList to store the elements in the list is doubly linked list. The internal data structure used by ArrayList to store the elements of the list is a dynamic array that can grow or shrink as the elements are added or deleted from the list.On the other hands, the list implemented by the LinkedList can’t be accessed randomly because for retrieving or accessing a particular element in the list you have to traverse the list. The list implement by the ArrayList can be accessed randomly because ArrayList adopts the index-based data structure of the array.Key Differences Between ArrayList and LinkedList in Java But the accessing is slower as it does not have index to directly access the elements. This is because if you add or delete any element in the list, then there is no need of shifting the elements as in ArrayList. In LinkedList, the manipulation of the list is easy and fast.
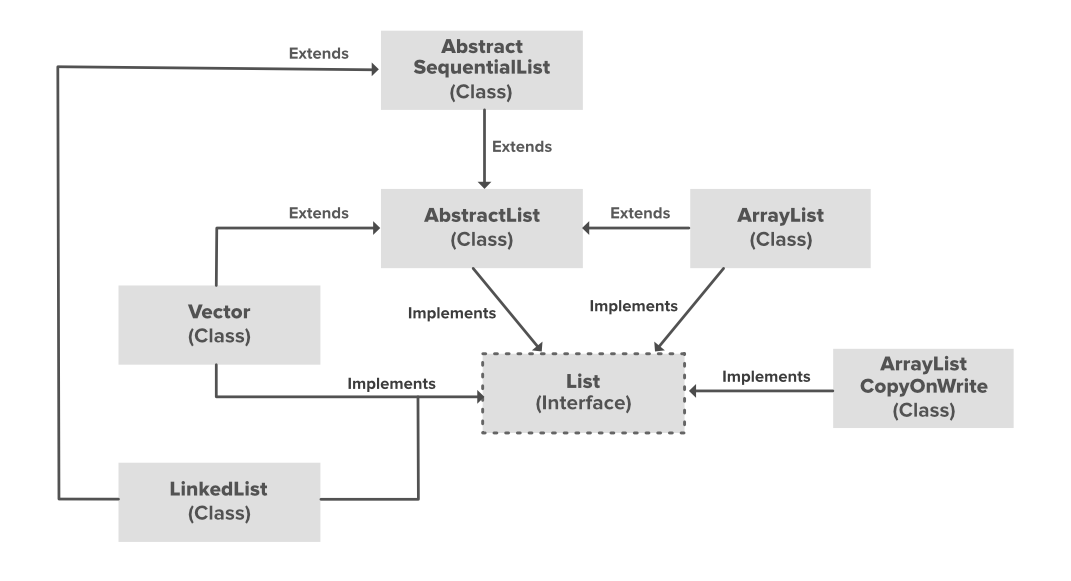
The second constructor creates a linked list, initialized with the elements of Collection c. The first constructor creates an empty linked list. There are two constructors in LinkedList class. If you want to retrieve any element from the list, you have to iterate the list in order to search that element. The linked list implemented using LinkedList can not be accessed randomly. The LinkedList class extends AbstractSequentialList and implements the List, Deque and Queue interfaces. Like ArrayList, LinkedList is also a Collection class uses doubly linked list as an internal data structure to store the elements in the list. Working with the ArrayList, sometimes you will require converting the Collection ArrayList into an array. The third constructor implements array list with the capacity provided in the argument. The second constructor implements an array list initialized using the Collection c elements. The first constructor implements an empty array list. There are three constructors of ArrayList: ArrayList( ) So knowing index you can directly access the eleemnt of the list. The array list implemented using ArrayList can be accessed randomly as ArrayList operates on the index-basis. But the array list implemented using ArrayList class can grow and shrink in size as the elements are added or deleted from the array. So you have to know the size of required array in advance. So it can not grow or shrink in size as the elements are added or deleted from the array. The need of ArrayList arises as the array in java is of fixed length. the array of variable length as a internal data structure to store the elements in the list. It extends AbstarctList and implements List interface. The AbstractList class is defined by the Collection Framework. LinkedList behaves as List a well as the Queue as it implements List and Queue both. Manipulation to elements in the list is faster in LinkedList.ĪrraylList behaves as List as it implements list. Manipulation to elements in the list is slower in ArrayList. LinkedList implements List, Deque, Queue.Īccess to elements in the list is faster in ArrayList.Īccess to elements in the list is slower in LinkedList. LinkedList extends AbstractSequentialList. The internal structure used to store elements is doubly link list. The internal structure used for storing elements is the dynamic array. LinkedList does not allow random access to the elements in the list. Content: ArrayList Vs LinkedListĪrrayList allows random access to the elements in the list. Let us discuss some more differences between ArrayList and LinkedList with the help of the comparison chart shown below. On the other hand, the LinkedList does not allow random access as it does not have indexes to access elements directly, it has to traverse the list to retrieve or access an element from the list. Both the classes are used to store the elements in the list, but the major difference between both the classes ArrayList and LinkedList is that ArrayList allows random access to the elements in the list as it operates on an index-based data structure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
